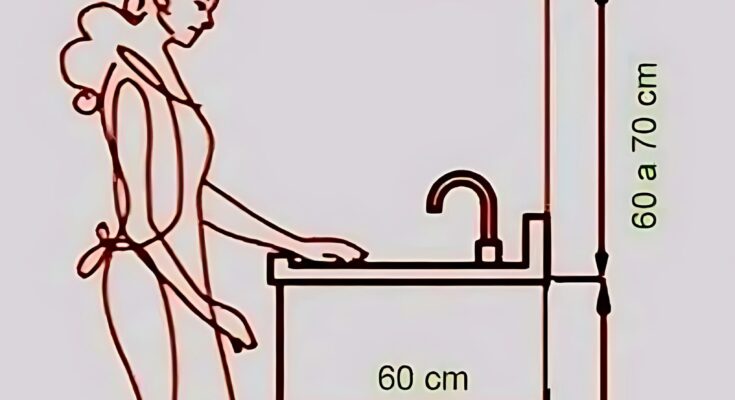
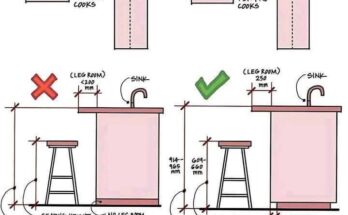
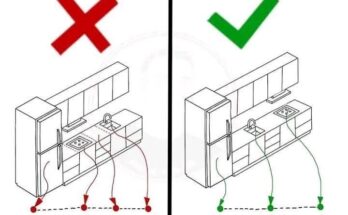
The ergonomic considerations and implications of the dimensions shown in the kitchen sink diagram, keeping in mind that these are general guidelines and individual needs may vary.
Detailed Breakdown of Ergonomic Aspects:
-
Countertop Height (90 cm / approximately 35.4 inches):
- This height is often considered a standard for standing work in kitchens for individuals of average height (roughly 5’3″ to 5’8″).
- Ergonomic Benefit: A properly heighted countertop minimizes bending at the waist, reducing strain on the lower back during tasks like washing dishes or food preparation.
- Potential Issues: This height might be too high for shorter individuals, leading to hunched shoulders and discomfort. Conversely, taller individuals might still need to bend slightly. Ideally, the countertop height should allow the user to work with their wrists straight and their forearms roughly parallel to the floor.
- Modern Trends: Increasingly, kitchen designs incorporate varying countertop heights to accommodate different tasks and user heights. For example, a lower section might be designed for kneading dough, while a higher section could be more comfortable for taller individuals or for tasks requiring more downward force.
-
Upper Cabinet Clearance (60-70 cm / approximately 23.6-27.6 inches):
- This vertical distance between the countertop and the bottom of the upper cabinets aims to strike a balance between accessibility of the upper cabinets and workspace visibility on the countertop.
- Ergonomic Benefit: Adequate clearance ensures that users have enough headroom while working at the sink and that they can easily see and access items on the countertop.
- Potential Issues: If the clearance is too small, users might hit their heads or feel cramped. If it’s too large, reaching items in the upper cabinets, especially the higher shelves, can become difficult and require awkward reaching or the use of a step stool. The optimal clearance can depend on the depth of the countertop and the height of the user.
- Accessibility: For universal design principles, considering adjustable height upper cabinets or alternative storage solutions can improve accessibility for individuals with different reach capabilities.
-
Upper Cabinet Depth (32-36 cm / approximately 12.6-14.2 inches):
- This depth is generally chosen to allow for sufficient storage of dishes, glasses, and other kitchen items without protruding too far into the user’s workspace.
- Ergonomic Benefit: A shallower depth reduces the need to reach deep into the cabinet, making items more easily accessible and reducing strain on the shoulders and back.
- Considerations: The ideal depth might depend on the size of the items being stored. Deeper cabinets can store more but can also make it harder to find items at the back. Pull-out shelves in upper cabinets can mitigate this issue.
-
Knee Space Depth (60 cm / approximately 23.6 inches):
- This horizontal distance from the front edge of the countertop to the front of the base cabinet (or any obstruction) allows space for the user’s knees when standing close to the sink.
- Ergonomic Benefit: Adequate knee space promotes a comfortable standing posture, allowing the user to get close to the work surface and reducing the need to lean forward, which can strain the back.
- Accessibility: For wheelchair users, a completely open knee space with sufficient height and depth is essential for rolling up to the sink. The diagram doesn’t explicitly show an open knee space, implying a standard base cabinet.
-
Toe Space (15 cm height / approximately 5.9 inches, 15-20 cm depth / approximately 5.9-7.9 inches):
- This recessed area at the bottom of the base cabinet allows the user to place their feet closer to the cabinet, improving posture and reducing strain on the lower back.
- Ergonomic Benefit: Toe space allows for a more natural and balanced standing position, preventing the user from having to stand further back from the countertop.
- Considerations: The height and depth of the toe space should be sufficient to comfortably accommodate most shoe sizes.
Additional Ergonomic Considerations Not Explicitly Shown:
- Sink Depth and Reach: The depth of the sink bowl should be considered to minimize splashing and the need to bend too deeply while washing dishes. The placement of the faucet and the reach required to access it are also important.
- Faucet Design: Ergonomic faucets are designed with easy-to-use handles and appropriate reach and spray patterns.
- Lighting: Proper lighting above the sink area is crucial for reducing eye strain and improving visibility during tasks.
- Flooring: Comfortable and slip-resistant flooring can reduce fatigue and the risk of accidents.
- Anti-Fatigue Mats: For individuals who spend long periods at the sink, anti-fatigue mats can help reduce strain on the legs and back.
In Conclusion:
The diagram provides a valuable snapshot of standard ergonomic dimensions for a kitchen sink area. By adhering to these guidelines, designers can create more comfortable and user-friendly kitchens. However, it’s crucial to remember that these are general recommendations, and the ideal dimensions can vary based on individual needs, preferences, and the specific tasks being performed in the kitchen. Universal design principles advocate for flexibility and adaptability to accommodate a wider range of users.